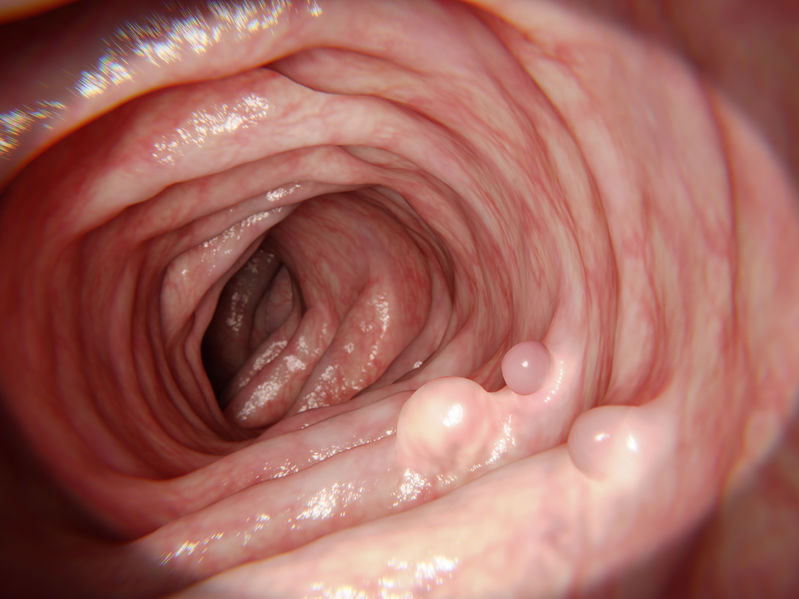
Gut Health
Scientific studies show that the gut microbiota is a big factor for several chronic diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, diabetes, heart disease and cancer.
Microbes in the gut produce vitamins, essential amino acid, short chain fatty acids and many other important byproducts from the food we ingest. Our gut doesn't just process food and create waste. It is a vastly complex chemical factory that influences every aspect of our health and mental status.
All disease begins in the gut, let food be thy medicine. (Hippocrates).
- The bacteria in our colon weigh 2-3 kilos!
- 60% of our stools are dead or alive bacteria.
- We produce 1-4 litres of gas from our gut each day.
- The human gut microbiota has 100,000,000,000,000 (100 trillion) micro-organisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoa. This is nearly treble the cells in our body.
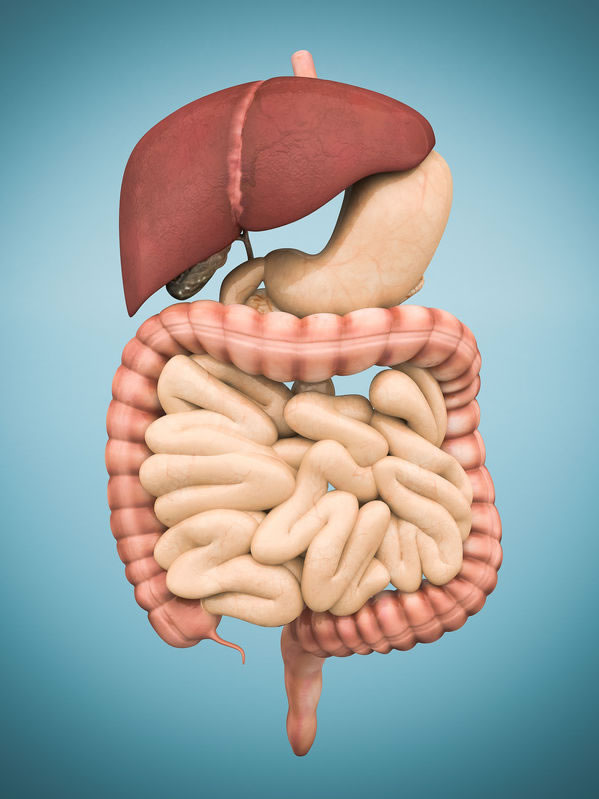
Most people have inadequate beneficial good bacteria, with excessive damaging bacteria. This is due to:-
- A poor diet.
- A lack of micro-nutrients.
- Taking antibiotics as a child.
- Taking antibiotics, birth control, NSAID’s, anti-depressants, antacids and other medicines.
- Infammation.
- Chronic stress which can alter gut secretion, permeability & leaky-gut, blood flow and sensitivity to foods.
- Toxins such as glyphosate pesticides, heavy metals and plastic additives & BPA.
- Poor bacterial acquisition at birth.
- Lack of exercise and obesity.
Your gut and the brain
Your GI tract contains 500 million neurons. These form the enteric nervous system (ENS) which is embedded in the lining of the gastrointestinal system (from your throat, all the way 9 metres to the anus. It can work independently of the brain, but the two are inter-twined. It's often called the second brain. You don't have to think to swallow and many gut functions carry on without thinking.
- More than 90% of the body's serotonin lies in the gut. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter and contributes to the feelings of well-being and happiness.
- 50% of the body's dopamine resides in the gut (L-dopamine is given to Parkinson's sufferers). Dopamine is a chemical messenger that carries signals between brain cells.
- Tryptophan is a precursor to the neurotransmitter serotonin and the hormone melatonin. Gut bacteria feeds on tryptophan in foods to reduce inflammation and produce important metabolites.
- Bifidobacterium species produce GABA which is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system
The gastrointestinal tract is sensitive to emotion, anger, anxiety, sadness and happiness. The brain has a direct effect on the stomach and intestines; for example, the thought of eating can release stomach acids before the food gets there. You may feel butterflies before an exam. Viewing a traumatic or gross event can make you physically sick. The vagus nerve, which controls messages to the gut as well as the heart, lungs and other vital organs is the gut’s direct connection to your brain. The gut also connects with the brain through chemicals like hormones and neurotransmitters that send messages.
- If your GI tract is in poor health, it can have a serious effect upon the brain. Tiredness, lack of sharpness, no desire, depression and neurological diseases can all follow. It can also lead to serious metabolic diseases that stem from chronic inflammation such as cancer and heart disease.
- There is a clear relationship between having mental health problems and having gut issues such heartburn, indigestion, reflux, bloating, pain, constipation and diarrhoea. Conversely, changes in the gut microbiota and inflammation in the gut can affect the brain and cause symptoms that look like Parkinson’s disease, autism, anxiety and depression. When the gut microbiota have been taken away in animal studies, it can cause death.
- Eating a nutritious diet is the most important thing a person can do to keep their gut healthy. Especially a varied source of fibre (these are called prebiotics because they feed your bacteria).
The large intestine (the colon)
The colon is the final stage of digestion and is the second part of the bowel, 6-8cm in diameter. It is a large tube that joins the small intestine. It travels up, across and down the abdomen (the ascending, transverse and descending parts). The final part of the colon is called the sigmoid. The sigmoid is a short S-shaped stretch of the colon, which leads to the rectum. Its main function is to store stools until they ready to enter the rectum. Inflammatory bowel disease such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease occur in the sigmoid. Diverticulitis, in which little outcrops of bowel (the opposite of a polyp) form and become inflamed, is more common in the sigmoid than any other part of the bowel. Small growths called polyps, as well as cancers, also favour the sigmoid.
The colon is much wider than the small intestine, but is also shorter, at roughly 6 feet long for an adult. Water and salts are removed from the waste as it passes through the colon. When the waste finally arrives at the sigmoid, it is stored until being forced by muscles into the rectum for a bowel movement.
The colon is not just a waste disposal system - it stores a vast amount bacteria. The stomach and the small intestine have relatively few types of bacteria, but the colon has an estimated 10 billion cellular micro-organisms per gram of content. Micro-organisms contained within the colon communicate with our immune system and participate in a variety of metabolic processes - we feed the microbes and they give us mutual benefits such as:
- Final calorie extraction.
- The production of short-chain fatty acids (bacteria give us 5-15% of our daily energy).
- Byproducts such as arginine and glutamine (critical amino acids).
- The synthesis of folic acid and vitamin K2.
- The cycling of bile acids.
- The prevention of pathogens.
- Regulatory T cells which modulate the immune system.
- Immune system boosting.
A low fibre / high carb Western diet is a disaster for your colon. The simple sugars get extracted by your small intestine, leaving the bacteria in the colon to starve. Hard-to-digest fibre travels to the colon as food for bacteria.
When a baby is born, its gut is completely sterile because the baby was fed via the placenta in the womb. During a normal birth, it picks up microbes from the mothers vagina. Just like the gut, the vagina contains of trillions of micro-organisms, mostly bacteria, plus some fungi and viruses. The primary colonising bacteria of a healthy vagina is called lactobacillus. It helps to keep the environment acidic and discourages other bacteria, yeast and viruses from thriving. More bacteria are added during breast feeding and from the non-sterile environment. When these natural events occur, the baby quickly develops a very diverse gut microbiota. By the age of two, a child's microbiota will resemble that of an adult. If babies are delivered by Caesarean section, they do not experience the mother's microbes. Bottle feeding formula milk will also reduce the baby's microbiota. But the biggest danger comes from antibiotics, which can destroy the child's gut microbiota. This of course is true for adults who take antibiotics. Modern antibiotics are very over-prescribed and are wide-spectrum, meaning that they kill many varieties of bacteria. Antibiotics can effect the brain development of children. Many believe that antibiotics are an underlying cause of autism. Behaviour and mood can change drastically after courses of antibiotics.
Our colon contains around 1000 strains of bacteria. The microbes in our gut contribute to our cognition and brain function For example it’s estimated that 90% of our serotonin is produced in the gut, and it’s been found that some of this serotonin is produced by four microbes (Candida, Streptococcus, Escherichia and Enterococcus). Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium produce gamma-Aminobutyric acid or “GABA” which is our chief inhibitory neurotransmitter which has anti-anxiety effects. Escherichia coli, Bacillus and Saccharomyces produce norepinephrine, a hormone involved in the fight or flight response. Bacillus and Serratia produce our motivation neurotransmitter, dopamine.
An unbalanced intestinal microbiota may affect the activation of the inflammatory pathways causing skin and joint problems such as psoriasis and even arthritis.
Cancer of the colon (bowel cancer)
The lifetime risk of developing colon cancer is about one in 20. However, this varies widely according to individual risk factors. About 70% of cases arise in the colon and about 30% in the rectum. It is one of the worst forms of cancer which contributes around 30% of total deaths from cancer. If caught early, it is highly treatable, but as with many other things in the medical world, the diagnosis and treatment can be worse than the actual disease.
Your colon is constantly being replaced. Every time you poo, it contains about 60% bacteria and also billions of cells from the wall of the colon. The cells that line the inner walls of the intestines and absorb the nutrients regenerate every several days.
Polyps occur naturally in the wall of the colon. A polyp is a small clump of cells that forms on the lining of the colon. Most colon polyps are harmless and this is where the problem lies in terms of very invasive colonoscopies and biopsies.
The growth and division of new cells is usually highly regulated. In some cases, however, new cells grow and divide before they're needed. This excess growth causes polyps to form. It is commonly thought that some polyps mastasticise and become cancerous. However most polyps are benign and harmless. Polyps can also get bigger, shrink or even disappear, this is due to the regenerative nature of the colon - billions of colon cells are lost and made each day.
Doctors and drug companies love expensive treatments. Colon cancer screening using colonoscopies and biopsies, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and surgery is very big business. Colon cancer is a dietary disease that is treated by medicine and surgery, not by changing diet. If you read the mainstream literature, this cancer it is blamed upon fatty diets, eating red meat and hereditary factors. They even say that you should eat more grains (grains are especially inflammatory).
The dietary advice given by governments and NGOs is terribly flawed, mainly because it's largely funded by food companies and big pharma. Screening and treatment for colon cancer is highly flawed (follow the money).
Colonoscopies
Colonoscopies are an invasive procedure that cause more harm than good, they are driven by money. It is a complex procedure and not just simply popping a camera up your rear!

- The procedure requires a thorough washing out of the colon with large doses of synthetic laxatives. This is followed by bowel irrigation with polyethylene glycol and electrolytes. This wipes out your gut microbiota. Once the bacteria have been wiped out you are instantly susceptible to chronic diseases. 2-3 kg of bacteria that took a lifetime to create - gone.
- It is a very invasive procedure that creates inflammation, tearing and perforation. The body will kick in a massive autoimmune response that can have long term serious effects and even lead to death.
- The risks of delayed bleeding, infection and ulceration are even higher.
- X-ray exposure from a single virtual colonoscopy increases one‘s lifetime risk of general cancer.
- Procedures performed under anesthesia are risky.
- Blood clotting increases the risks of stroke, heart attack and pulmonary embolisms.
- Doctors miss many polyps and even fully developing tumors. Some doctors perform dozens of colonoscopies daily at a cost of $3000, so speed is important. Colonoscopies are done under anesthesia so that the tube can be rammed in quickly.
- In the US, when a patient presents with rectal bleeding or other symptoms consistent with colon cancer, it is within the standard of reasonable care to recommend a colonoscopy (they can be sued if they don't). Colonoscopy lawsuits are a big industry in the USA, but doctors see this as cost of doing business.
- There are no regulations for cleaning colonoscopy scopes or maintaining the equipment and this often leads to complications and contamination.
- In the US, 15 million colonoscopies are done annually. The incidence of colon cancer is on the rise (due to diet and terrible sedentary lifestyles) and this will mean a windfall for the hospitals as the screening will be lowered.
- According to the report “Complications of Colonoscopy in an Integrated Health Care Delivery System,” the combined injury and kill-rate of colonoscopy-related complications is 0.5 percent, or about 70,000 per year in the US. 50,000 die each year from colon cancer and rectal cancer combined.
- Sigmoidoscopy only looks at the lower part of the colon and is therefore less invasive.
- Polyp removal and biopsies are common. Some early stage colon tumors and most polyps are removed during a colonoscopy. The removal of the polyp causes scarring, bleeding and huge inflammation which can cause even more complications.
- Surgery occurs when the polyps are too large to be removed during a colonoscopy.
Surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy for colon cancer
When polyps are too frequent or large, or if cancerous tumours exist, portions of the colon can be removed via surgery. This is called a "resection or colectomy". The complete removal of the colon could result in a colostomy, where the faeces are passed into an external bag. the repercussions of this procedure are huge and so it should be avoided at all cost.
Chemotherapy as a treatment for colon cancer has a poor success rate. Chemotherapy probably causes or hastens death rather than treat the underlying cancer. Highly toxic chemo medications often give patients just a few more months of life, often or kill them prematurely or cause more cancer down the line. Chemo drugs have a disastrous effect upon the gut microbiota.
Radiotherapy sends intense focused beams of radiation into the colon to try and kill the cancer cells. The radiation induces dysbiosis (microbial imbalance or bad adaptation), causing injury and intestinal inflammation.
So the conventional options for suspected colon cancer are pretty devastating. However they all ignore the real reasons that the polyps, lesions and growths develop in the first place. This is bad nutrition, toxins and the neglect of the microbiota. Simply removing a polyp does not treat the cause, nor does it actually remove all the offending tissue.
CTC Scans (virtual colonoscopies)
With a CTC scan (also known as virtual colonoscopy), doctors can view the colon just like an x-ray. CTC is a medical imaging procedure which uses x-rays and computers to produce 2D and 3D images of the colon. It is totally non-invasive, but you still need to take laxatives and enemas to clear the colon (flushing away the microobiota).
Studies have shown that virtual colonoscopy has detection rates similar to traditional colonoscopy for cancer and most types of polyps. In other words, many are missed! If polyps are found then it might not be the end of the world, because if you do a M2-PK stool test and the enzyme biomarker M2-pyruvate kinase (an enzyme produced by colorectal cancers) is negative then
- Patients with larger polyps are referred for endoscopic follow-up and removal. The way better option is polyp surveillance. This is when the scan is repeated and the scans compared.
- If the first scan showed problems, you should do a complete lifestyle change (see, What if I was diagnosed with colon cancer below) and then get re-scanned after 2-3 months. You can then follow up with monthly M2-PK stool tests.
The only 2 problems with the CTC imaging is that it will expose your body to radiation and slightly increase your overall cancer risk (but this risk could be counter reduced by following colon-friendly lifestyle changes). The second BIG problem is that it requires your colon to be flushed. Perhaps the best way to fix this is to have your own faeces replanted or get donor faecal matter (see below - it works).
Testing for colon cancer
 There is a simple non-invasive test for the early detection of colon cancer, called the M2-PK stool test. The enzyme biomarker M2-pyruvate kinase is an enzyme produced by colorectal cancers. The detection of M2-PK relates to changes in the tumour metabolism (tumours love to feed on sugar via a process called glycolysis). The test is able to detect both bleeding as well as non-bleeding colorectal cancers and polyps. A colonoscopy can only see a protruding polyp, but this test can detect non-protruding cancers in the colon. Studies show an accuracy of around 95% in detection rates. If the test come out positive, the recommendation is to have a colonoscopy. We think that this is wrong, given the damage to the colon that would be cause. If the test is positive M2-PK, then you should consult a doctor and you would need to make your own judgement on ruining your gut.
There is a simple non-invasive test for the early detection of colon cancer, called the M2-PK stool test. The enzyme biomarker M2-pyruvate kinase is an enzyme produced by colorectal cancers. The detection of M2-PK relates to changes in the tumour metabolism (tumours love to feed on sugar via a process called glycolysis). The test is able to detect both bleeding as well as non-bleeding colorectal cancers and polyps. A colonoscopy can only see a protruding polyp, but this test can detect non-protruding cancers in the colon. Studies show an accuracy of around 95% in detection rates. If the test come out positive, the recommendation is to have a colonoscopy. We think that this is wrong, given the damage to the colon that would be cause. If the test is positive M2-PK, then you should consult a doctor and you would need to make your own judgement on ruining your gut.
What if you are diagnosed with colon cancer?
Take a different approach to conventional medicine. A complete lifestyle change should be attempted first:-
- No colonoscopies and no drugs.
- Find a non-mainstream doctor that knows about the colon. Or find a good hospital (anywhere in the world) that would help with an alternative strategy.
- Spend hours researching.
- Dry and electrolyte fasting promoting big weight loss and autophagy. Long fasts interspersed with clean focused eating, based on a tight eating window.
- Exercise and abdominal massage.
- No alcohol.
- No sugar.
- Ketogenic style diet (between fasts) consisting of anti-inflammatory foods and anti-cancer foods.
- Every food item would be 100% organic and pastured.
- A diet rich in herbs and natural spices such as turmeric, ginger, garlic, ginseng, parsley and olive leaf.
- Find a hospital with the best CTC imaging system with 3D scans. I would repeat this after 2-3 months of a total lifestyle change and see the comparison.
- Pre-biotic food intake.
- Fermented food protocol.
- Drink bone broth and focus upon collagen and amino acid intake.
- Megadoses of vitamin C, vitamin E, vitamin D, vitamin B's and anti-oxidants such as caretenoids.
- A perfect micro-nutrient profile, particularly magnesium, calcium, selenium, iodine, zinc and boron.
- Cold and hot shock therapy.
- Stress reduction and breathing exercises.
- Focus on sleep.
- Do a fecal microbiota transplant from a great donor. Even do a DIY version if pushed!
- Do constant stool tests plus some genetic testing to investigate possible genetic factors.
- Consider hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
Colon cancer is a dietary disease that can be cured with food and lifestyle changes.
How to improve your gut health and microbiota
- Feed your bacteria with prebiotics: You need complex carbs via fibre that makes its way down to the colon in order to feed the bacteria. Vegetables are also one of the best forms of dietary fibre. Seed husks, flax seeds, hemp seeds, Jerusalem artichokes and chia seeds provide valuable sources of soluble and insoluble fibre that nourish your healthy gut bacteria and lower your risk of colon cancer. Prebiotics act like a fertiliser, boosting the growth of 'good' bacteria.
- Only take antibiotics in an emergency. Look at more natural remedies for minor ailments. Wide spectrum antibiotics are particulary damaging to butyrate-producing species of bacteria (butyrate is a precursor of a ketone that is used for energy). Children are particularly vulnerable to antibiotic gut microbiota damage, causing them to become fat and show autistic & behavioural patterns.
- Eat probiotic foods: These are foods that contain live bacteria., such as yogurts. Cheeses are great, such as gouda, mozzarella, Cheddar, cottage cheese, and feta (which is filled with lactobacillus plantarum, known for producing antinflammatory compounds). There is a complex sugar called a fructooligosaccharide (FOS) which goes straight to the gut. FOS containing foods are bananas, onions, chicory root, garlic, asparagus, jícama, konjac and leeks. Inulins are a group of naturally occurring polysaccharides produced by many types of plants (same as the FOS foods). Breast milk contains inulin solely for the purpose of feeding the babies microbiota!
- Eat fermented foods: Foods that have been fermented contain many micro-nutrients as well as billions of bacteria. Choose foods such as natural yogurts, kimchi, sauerkraut, natto and blue cheese, natto is an amazing fermented food because it contains vast amounts of vitamin K2. Sauerkraut is also super high in vitamin C. The microbes in fermented foods are also far more likely than most other bacteria to make it safely down into your colon, because they are extremely resistant to acid, having developed in an acidic environment.
- Stop smoking: Smokers have a double risk of developing colorectal polyps according to a study. But smoking is bad for most cancers as it diverts the bodies immune system to be constantly fighting the toxins inhaled and swallowed. Most people believe that they are just inhaling smoke, but the chemicals are being ingested.evidence demonstrates that smoking is the most important environmental risk factor in Crohn's disease and it contributes to ulcerative colitis. Cigarette smoke is considered to be the most important environmental risk factor in IBD pathogenesis.
- Cut out sugar and processed carbs: Sugar and HFCS is in 70% of processed foods.
- Take lots of vitamin C: Two-time Nobel Prize winner, Linus Pauling, was a lifelong advocate of vitamin C. Linus Pauling recommended large doses of vitamin C which is needed to make collagen in your body. Low vitamin C causes scurvy, which is the breakdown of arterial walls caused by lesions. Vitamin C also has a protective effect in the intestines. It also has cancer reducing properties via lowering inflammation.
- Take plenty of magnesium: Studies have shown that high magnesium intake is associated with a decreased risk of colon cancer. A 100mg increase in magnesium lower the risk by 12%.
- Take plenty of potassium because it's critical for stomach acid production. The very low pH of gastric juice (pH of 1) is the result of H+ and Cl- ion secretion (hydrochloric acid production) by cells in the walls of the stomach. Each day, these cells secrete 1-2 litres of HCl. Potassium ions play a vital role because they exchange with H+ ions. The gastric hydrogen potassium ATPase (gastric H+-K+-ATPase) pumps H+ ions into the stomach and takes up K+ in return. No other tissue in the body builds higher concentration of H+ than the stomach wall. There is a one million-fold enrichment of H+ in the gastric juice, which is unique amongst animals.
- Get plenty of sunshine and vitamin D: Vitamin D deficiency increases the risk of colon cancer. UVB exposure from the sun, and/or vitamin D3 supplementation can get your vitamin D levels higher. Don't take statins as these reduce your cholesterol which is needed for vitamin D production (and bile acid). A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition evaluated calcium and vitamin D3 in preventing cancer. After just one year of vitamin D3-added supplementation, the risk of developing all cancer types was decreased by 77%.
- Get plenty of iodine. The thyroid gland needs iodine to make hormones. If the thyroid doesn't have enough iodine to do its job, feedback systems in the body cause the thyroid to work harder.
- Eat pears, which are high in dietary fibre, containing 6g per serving. This high dietary fibre content sets pears apart from other fruit in terms of beneficial effects on gut health. Pears are high in pectin and other soluble fibres, with pears containing 70% insoluble fibre and 30% soluble fibre. Pectin is a naturally occurring polyscaccaride (a complex sugar) found in berries, apples and other fruits. Polysaccaries are great for the gut bacteria. In a NCBI study, pectin was shown to have a low degree of esterification and its enzyme segments allow adhesion to the mucous in the gastrointestinal tract. Pectin forms a physical barrier protecting microbial invasion during stress and SIBO.
- Focus upon improving collagen production: Your gut is made from collagen. Old tennis rackets and violin strings were made from sheep guts. You can boost your collagen production by taking bone broth and some amino acids. Vitamin C is vital for collagen production, which is why your gut (and arteries) will deteriorate without adequate vitamin C (called scurvy). Statins will destroy your collagen.
- Make sure the essential electrolytes are in abundance (Sodium, potassium and magnesium). Kidney issues will mean that your colon will process potassium and sodium as stools.
- Don't take statins. They are poisons. They reduce cholesterol which is used in many essential bodily functions such as vitamin D production, hormone production and collagen synthesis. A recent study published in Nature has found that statins disturb the gut microbiota. Statins inhibit the growth of useful bacteria in the gut and allow other bacteria to flourish and become superbugs resistant to antibiotics.
- Don't take antacids and pills for indigestion.
- Avoid processed foods: Particularly cheap processed meats. Your meat intake should come from quality sources such as grass fed animals.
- Avoid gluten and grains. Quinoa might be a good alternative.
- Exercise: Regular exercise can significantly reduce your risk of colon cancer. Being physically active reduces colon cancer risk by 30-40%. Excessive sitting down also creates blood supply issues to the abdomen, which can cause gut issues.
- Don't eat all day long! This creates constant insulin spikes which increases your overall cancer risk. When the body is constantly fed carbs it cannot trigger autophagy (cellular cleaning) and apoptosis (programmed cell death). Doing some intermittent fasting and particularly fasting will boost cellular repair and boost your immune system. Sleep and exercise also boosts autophagy. Cancer cells also love glucose (cancer cells have 10x the number of insulin receptors and can metabolise glucose aerobically or anaerobically). Research continues to show that sugar is the main source of fuel which feeds cancer and contributes to an inflammatory environment. Sugar essentially increases the risk for cancer and disease.
- Exercise. HIIT exercises are perfect to get the abdomen moving. Study after study show that active people have a much healthier gut flora than sedentary people.
- Lose weight: Studies have linked obesity to an increased risk for many different cancers, including colon cancer. If you’re overweight or obese, and are at risk of colon cancer then you must drop the weight quickly. Fasting is the number one method to lose weight whilst maintaining you metabolism. Morbidly obese people who opt for bariatric surgery, such as gastric bands, have a drastically altered microbiota.
- Avoid endocrine disruptors and toxins: Anything you swallow enters your gut, it will either pass through or be absorbed. BPA & phthalates in plastics pose a big risk.
- Avoid inflammatory foods: Sugar, high fructose corn syrup, trans fats, rancid fats, PUFAs, processed meats, refined flours, wheat and gluten, vegetable oils, fried foods, diet sodas, additives & preservatives.
- Avoid artificial sweeteners. Whether it is sucralose, aspartame, or saccharin, it seems that all synthetic sweeteners affect the bacteria in the gut and damage the intestinal wall.
If you have children
One of the worlds leading microbiota experts (Prof. Simon Carding) ended a lecture by giving some great advice (the first 4):-
- Buy then some pets.
- Let them roll around in mud.
- Let them eat mud.
- Maximise their exposure to dirt and microbes.
- Let them play outside.
- Get them off their phones and gadgets in your super clean house.
- Let them climb trees and run around.
- Stop washing them all the time.
- Stop using anti-bacterial cleaners around the house.
- Use simple washing flakes for washing clothes.
- Get rid of all environmental toxins from your home
- Make your own toothpaste.
- Feed them varied natural foods and throw out all the processed foods.
- Get them to eat to low glycemic index fruits.

Fasting and the gut microbiota
There is some evidence that fasting may have some effect upon gut microbiota diversity. The microbes in the colon need food. But with a decent diet that contains fibre that passes all the way through to the colon, fasting should not have a detrimental effect. The truth is that fasting is hugely beneficial to gut issues, including cancer. If you have some serious gut issues such as IBS, you could spend months with elimination diets trying to find the culprit. But fasting for several days can reverse IBS without any effort.
Fasting boosts your immune system and your cellular cleaning mechanisms. Every day we produce millions of potentially cancerous cells - these are simply hoovered up by the bodies natural systems such as autophagy. But when the immune system is compromised, the cancerous cells can escape the net and mastecise into groups of cells that can grow into colonies.
If you ask a doctor about fasting they will give you medicines or offer surgery! Taking breaks from food is one of the best heath boosting tools you can use.
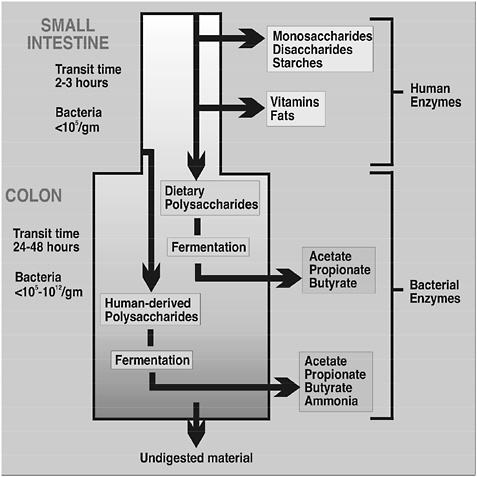
A good strategy just before starting a 48+ hour fast (not intermittent fasting) is to eat some polysaccharides and complex fibre during your last couple of meals. Transit time through the GI tract can be up to 48 hours, so you can easily do 3-4 day fasts without any impact on your microbes. Your body will be in ketosis 16-24 hours after you start the fast and you will get all the fat burning benefits.
Another good option is to do some hard cardio at the start of your fast - this will deplete your muscle and liver glycogen stores and hasten the onset of ketosis and autophagy.
Leaky Gut
Leaky gut is increased intestinal permeability, possible caused by lesions or weaknesses in the intestinal wall. This could let substances leak into the bloodstream. When this happens, the body triggers an auto-immune reaction to deal with the foreign substance. The whole condition is open to some debate.
The intestinal walls are made of collagen. Bone broth and gelatin have long been used to heal digestive problems, due to their collagen content. Collagen synthesis is an essential process for repairing the intestinal lining. Vitamin C is critical for collagen production. You are constantly losing gut lining and the intestinal cell need constant replacement.
Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis occurs when the diverticula (folds and pouches) become inflamed or irritated and infected. Diverticular bleeding occurs when a small blood vessel within the wall of a diverticulum bursts. Diverticulitis with mild symptoms usually requires a person to rest and follow a good gut protocol (such as fasting). But sadly, doctors are often too quick to prescribe antibiotics with the resulting damage to the gut flora. This solves a small problem by creating a bigger one.
Doctors may also prescribe pain relief such as paracetamol (Tylenol) and NSAIDs such as asprin and ibuprofen which all have terrible effects upon the gut.
- Paracetamol destroys your cellular antioxidant Glutathione.
- Asprin can cause intestinal bleeding.
- Ibuprofen can cause leaky gut and ulcers.
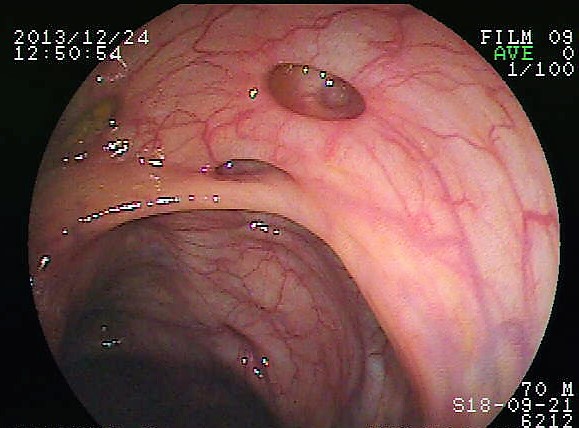
Colitis
Colitis is a chronic digestive disease relating to the inflammation of the inner lining of the colon. When your immune system tries to fight off an invading virus or bacterium, an abnormal immune response causes the immune system to additionally attack the cells in the digestive tract. Ulcerative colitis is one form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Colitis comes and goes and sufferers often get nasty flares (Small ulcers can develop on the colon's lining, and can bleed and produce pus).
Inflammatory processed foods are a known trigger of colitis, but the underlying cause is a weakened gut microbiota (dysbiosis). Researchers found that a protein called NLRP12 suppresses inflammation in response to bacterial components, and that provides protection against colitis and colitis-related colon cancer.
- Crysin is a natural flavone commonly found in many plants (and honey). Polyphenolic compounds, especially flavonoids, are known as the most common chemical class of phytochemicals, which possess a multiple range of health-promoting effects, providing an essential link between diet and prevention of several diseases. Honey helps with ulcerative colitis is due to the crysin content (Manuka honey and other quality honey).
- Apigenin is a naturally occurring compound with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer properties. Research show that apigenin was an effective treatment against chronic ulcerative colitis. Apigenin is found in parsley, onions, celery, grapefruit and chamomile tea.
- There are also beneficial foods that reduce inflammation and help with nutrient absorption, like omega-3 foods (including fish oil) and probiotic foods. Top probiotic and fermented foods include kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, natto, probiotic yogurt, miso, kombucha and raw cheese.
- A major symptom of ulcerative colitis is anemia, which occurs when the body doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells. So eat iron rich foods.
- Folate (vitamin B9) is another important vitamin for people with ulcerative colitis because it helps the body make new cells. A folate deficiency causes anemia, poor immune function and poor digestion (chickpeas, lentils, asparagus, avocado, beetroot and broccoli are great for folate).
- Eat turmeric due to the anti-inflammatory compound called curcumin. Throughout history, turmeric was used to treat bowel issues.
- Eat ginger (anti-inflammatory).
Gut biodiversity
The bacteria in your gut must be diverse so they can have a wide spectrum effect. The more types of bacteria you have, the more resilient you become to disease, especially as you get older. A diverse microbiota protects against pathogens, extracts nutrients and energy from our diets and contributes to our immune function. Dysbiosis is the disruption of the normal balance between the gut microbiota and host. This has been associated with obesity, malnutrition, inflammatory bowel syndrome (IBS), neurological disorders and cancer. Think or bacteria as musicians. Listening to an orchestra is better than listening to a string quartet.
Stool transplants (FMT) and "crapsules"
 People with severely damaged microbiota, or have chronic gut issues, could benefit from feecal microbiota transplant. This is the process of transplantation of fecal bacteria from a healthy individual into a recipient, in order to restore or alter the gut microbiota. Only 4% of FMT donors are eligible to meet the strict criteria and they get paid $40/stool in some cases. This high screening was due to a woman becoming severely obese after receiving FMT from her obese sister. The technique actually goes back thousands of years, with the Chinese drinking "yellow soup" made from fermented human stools.
People with severely damaged microbiota, or have chronic gut issues, could benefit from feecal microbiota transplant. This is the process of transplantation of fecal bacteria from a healthy individual into a recipient, in order to restore or alter the gut microbiota. Only 4% of FMT donors are eligible to meet the strict criteria and they get paid $40/stool in some cases. This high screening was due to a woman becoming severely obese after receiving FMT from her obese sister. The technique actually goes back thousands of years, with the Chinese drinking "yellow soup" made from fermented human stools.
FMT has been used experimentally to treat other gastrointestinal diseases, including colitis, constipation, irritable bowel syndrome, and neurological conditions such as multiple sclerosis and Parkinson's. FMT can be done by:
- Inserting the fecal matter into the colon through the anus.
- Delivering the poo into the stomach via a feeding tube.
- Taking a slow release poo capsule, "crapsule", that releases the poo into the intestine.
It seems quite extreme, but the technique actually works. People who have been close to death through C. difficile infections have made a full recovery. The C. difficile cure rate is 95% for FMT. The restoration of the gut flora via FMT can cure may gut related issues. A child with autism or ADHD that has a bad gut microbiome would vastly improve with FMT.
Eating poo has never killed anyone, but colonoscopies kill tens of thousands each year.
MTHFR gene
An MTHFR mutation is a problem with poor methylation and enzyme production. MTHFR mutations affect every person differently and it’s believed that up to 30-50% of people might carry a mutation. MTHFR is a gene that provides the body with instructions for making a certain enzyme called methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. An MTHFR gene mutation can change the way some people metabolize and convert important nutrients from their diets into active vitamins, minerals and proteins. Digestive complaints are common among people with MTHFR A1298C mutations. Many things affect digestive health, including nutrient intake, inflammation levels, allergies, neurotransmitter levels and hormone levels. Leaky gut syndrome can make problems worse by harming the normal absorption of nutrients and raising inflammation.
- Having a healthy gut is especially important for people with MTHFR issues.
- Consume more natural folate (vitamin B9), Vitamin B6 and Vitamin B12.
- MTHFR C677T and A1298C gene mutations are the most common and the ones that are typically tested.
- IF YOU HAVE AN MTHFR ISSUE - YOU MUST PAY SPECIAL ATTENTION TO YOUR OVERALL GUT HEALTH.
Pooing
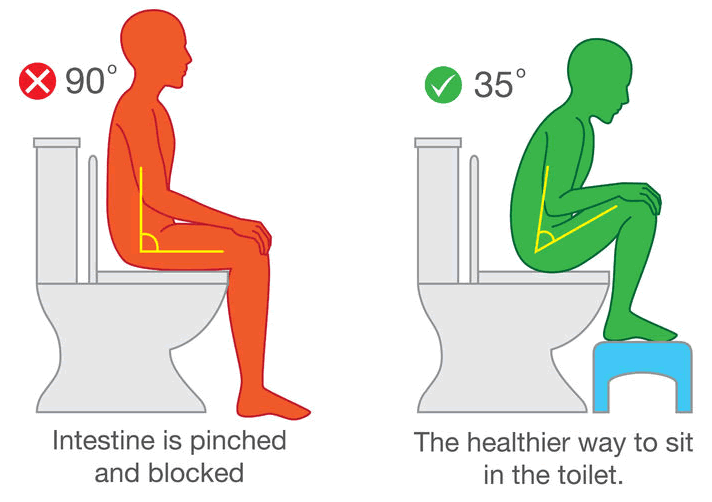
When sitting on the toilet, with knees at 90 degrees, your puborectalis muscle is only partially relaxed, but in a squatting posture it releases completely. Humans are designed not to leak, when we are upright there is a bend in the pipe between the rectum and anus which stops us pooing easily. Squatting opens the pipes and frees the poo without the need to push hard.
- Pushing hard is and straining is bad for you as it builds pressure which can promote diverticulitis.
- Holding on for too long is bad for you.
- Holding in wind is also bad.
You can mimic a squatting position by putting a stool (the furniture version!) under your feet. We have evolved to squat whilst pooing, so you should get back to doing what nature intended.
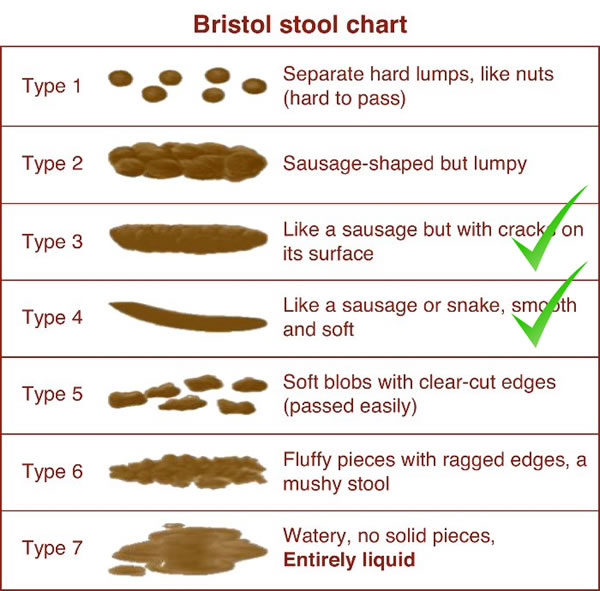
A healthy gut should be producing type 3 & 4 stools. Type 1 & 2 show constipation which can occur during times of stress, dehydration or being sedentary. Type 5-7 are loose stools. Loose stools after eating can be an indication of food poisoning, lactose intolerance or an infection. Certain foods, such as spicy or oily foods, can also create loose stools, but if your diet lacks fibre. Chronic loose stools could indicate:
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Celiac disease.
- Ulcerative colitis.
If your stools are yellow of lighter in colour, this may indicate cirrhosis of the liver, gall bladder issues or hepatitis. These reduce or eliminate bile salts that help the body digest food and absorb nutrients. Gallstones reduce the amount of bile that reaches your intestines. Not only may this cause pain, but it can also turn your stool yellow.
The presence of blood in the stool is very serious. It is commonly caused by gastroenteritis which is an inflammation of the lining of the intestines caused by a virus, bacteria or parasites. Seek medical help but be very wary of antibiotics or any screening methods offered.
Abdominal self massage is very beneficial to your gut, and it's easy to do yourself. start below your sternum, with one whole hand, move down your abdomen with a downward stroke and follow with the other. Use your fingertips and gently massage in small circular motions. Move from the sides inward and downward. Lying down on the floor or in a bed is best.
The link with autism and children
Antibiotics have been both a blessing and a curse. Antibiotics are given far to readily, especially to children. We think of the main problem as being the development of resistant bacteria, but one of the main issues is the devastating effect antibiotics have upon upon the gut microbiota. Wide spectrum strong antibiotics are given to babies and children with not mention of gut health to parents. Our microbes produce essential micro nutrients that are both neuro-protective or essential to the brain. When these microbes are removed, there can be several unforeseen issues that can affect a child's developing brain.
Autism rates have soared in the past few decades, and the link to antibiotic use has been largely ignored. How many parents are told that their babies antibiotics (or vaccines) could lead to brain serious brain injury? Autism has rocketed to epidemic levels due to:
- The use of wide spectrum antibiotics in small children.
- The use of neuro-toxic vaccines in multiple doses (US children get 72 doses of 17 vaccines).
- Environmental toxins such as glyphosate and fluorinated chemicals.
Is the appendix essential?
Our appendix is often described as a non-essential body part that was once used thousands of years ago. But new research has shown that the appendix acts as a reservoir for gut bacteria. In the event of a catastrophic loss of bacteria, such as in cholera or severe diarrhoea, your gut bacteria can be restored from the appendix. The appendix sits at the junction of the small and large intestines, it measures around four inches, and sits in the lower right your abdomen.
It can easily become infected and cause a crippling appendicitis, which can lead to a burst. This is why doctors often remove the appendix. So if you suffer from an appendicitis, you should not immediately go for appendix removal. While taking antibiotics is not highly advisable, it may be the lesser of the two evils if you compare it to surgery. Make sure you take prebiotics and probiotics after a course of antibiotics. Have your gut microbiota tested afterwards.
Source: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov,