Olives
Olives are a major component of the Mediterranean diet. People from the Mediterranean who consume olives and olive oil have a longer life expectancy and lower risks of heart disease, high blood pressure and stroke compared with North Americans and other Europeans.
- Vitamin E: Olives contain high amounts of this powerful antioxidant.
- Iron: Black olives are a good source of iron, which is important for the transport of oxygen in red blood cells (8).
- Copper: This essential mineral helps the body form collagen and absorb iron, and plays a role in energy production. Most copper in the body is found in the liver, brain, heart, kidneys, and skeletal muscle.

The antioxidants in black olives help to prevent heart disease. Olives contain healthy monounsaturated fat which has been found to lower the risk of heart disease and increase good cholesterol. There are close to 2,000 varieties of olives grown across the world, the two main types of olives are black olives and green olives.
Nutritional Value Of Olives
The health benefits of olives mainly come from the excellent micro-nutrient content: iron, calcium, fiber, copper, vitamin E, vitamin K, choline, sodium, phenolic compounds and omega-9. Olives are a rich source of antioxidants such as oleuropein, hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, oleonalic acid and quercetin.
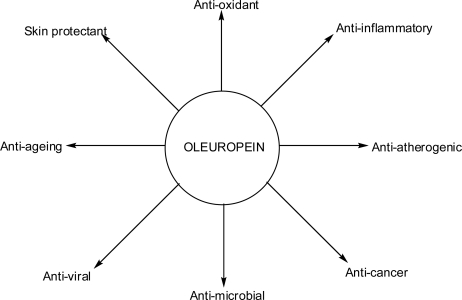
Oleuropein
Oleuropein is a type of phenolic bitter compound found in green olives, olive leaves, and argan oil. Olives contain oleuropein which has been shown to promote vasodilation (the process by which blood vessels relax and expand to accommodate the blood moving through the vessels, aiding men to achieve erections). It also help enhance production of nitric oxide (NO), the messenger molecule in the endothelial lining of the blood vessels that causes vasodilation. Oleuropein is very abundant in the early stages of olive growth in young green fruits.
Oleuropein, the main glycoside present in olives, and hydroxytyrosol, the principal degradation product of oleuropein present in olives, have both been linked to reduction of coronary heart disease and certain cancers.