Drinking Guide
Alcohol is not required for any bodily process. When you drink alcohol, 10% goes to the brain, 10% gets processed in the intestines and the majority (80%) goes straight to the liver to be metabolised. Many beers contain carbs (usually maltose) which also need to be metabolised or stored as fat. When your body takes in carbs, the glucose gets metabolised throughout the body and only 20% gets to the liver. So you can see that drinking alcohol makes your liver work 4 times harder.
Are you getting the majority of your calories from alcohol?
Look at the following table of common beers and you will realise that drinking 7 small beers (4 pints) is going to clock up around 1000 calories. The same goes for 5 or 6 Jack Daniels and cokes. This will eat up virtually half of your daily calorie allowance. It would take a 70 minutes brisk jog to burn all that off. It's not even that hard to go through 8 pints in an evening (2000 calories).
Drinking alcohol is inevitable for most people, so we should look critically at strategies to maximise the fun and minimise the harm it causes.

Mixers could be the problem?
Look at the mixers below. You can see the grams of sugar in a typical 125ml serving. A spoon full of sugar (one sugar lump) weighs 4g so the mixers are adding about 3 spoon fulls of sugar (50-60% fructose) to your drink. Ten Jack cokes in a night will add 34 spoon full of sugar to your body. Not to mention the 1900 calories! Please don't think that fruit juices are good for you!

Alcohol & the liver
When you drink alcohol, 10% goes to the brain, 10% gets processed in the intestines and the rest (80%) goes straight to the liver to be metabolised. Many beers contain carbs, such as maltose, which also need to be metabolised by the liver or stored as fat. When your body takes in carbs, the glucose gets metabolised throughout the body and only 20% gets to the liver. Drinking alcohol immediately makes your liver work 4 times harder.
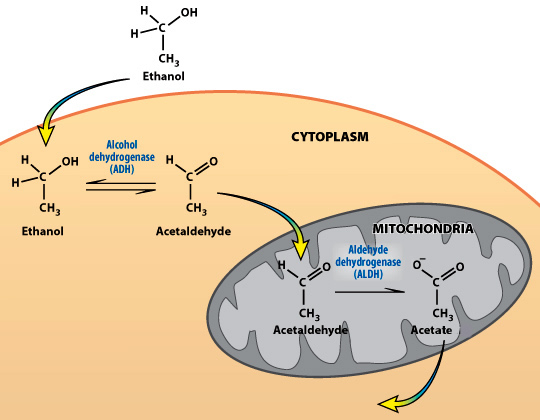
Ethanol does not need insulin to get into the cells, so it diffuses into the liver cells. The liver converts the ethanol to acetaldehyde which is poisonous to the body. It's the acetaldehyde that contributes to a hangover. Acetaldehyde creates "reactive oxygen species" or ROS. These cause tissue and protein damage and make heavy drinkers look older. The mitrochondria in the liver convert acetaldehyde into acetate which is then either:
- Passed into your bodies energy cycle.
- Converted into fat.
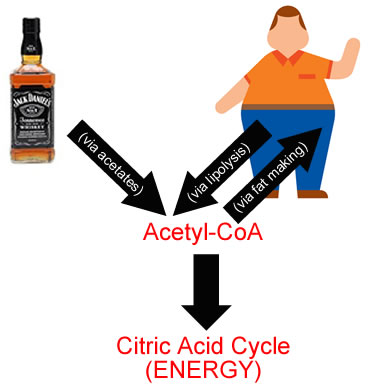
Tons of acetate needs to be processed in the mitochondria by the citric acid cycle. This is then converted into acetyl-CoA which ultimately produces energy, carbon dioxide and water.
Acetyl-CoA can be produced from the alcohol route (via acetate) or via the β-oxidation of fatty acids (fat burning). But when you drink alcohol you are not going to be burning fat! Too much alcohol hitting the liver will put it into overload as you can only convert so much of it to energy (unless you are jogging with a beer!). Your liver has no choice but to take the Acetyl-CoA and start lipogenesis (fat creation).
If you are inactive and drink a lot of booze, or sugary drinks containing high fructose levels, your liver will produce fat as tiny lipid particles. when too many are produced the fat stays inside the liver which then become fatty.
Fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
So if our liver has to resort to lipogenesis and make new fat, some of the lipid droplets end up being trapped in the liver, leading to a fatty liver (similar to fois gras, which is the liver of a goose that has been force fed carbs to get the liver fat and creamy). This can happen due to:
- Long term alcohol consumption.
- Fructose consumption (usually from excessive sodas and sugary drinks).
Fatty liver leads to high cholesterol, high levels of blood triglycerides, metabolic diseases, obesity (particularly fat around the abdomen), polycystic ovary syndrome, sleep apnea and type 2 diabetes. But there is good news, fatty liver can be reversed with a good diet and fasting.
Fructose + Alcohol is a deadly combination
- Alcohol is processed mainly in the liver.
- Glucose can bypass the liver and be processed throughout the body.
- Fructose can only be processed in the liver.
- Mixers and juices for drinks contain huge amounts of sugar.
Always try and add some ice
Drinking beer straight from the bottle is quite common, but you should consider trying a chilled glass with some ice. You will effectively be watering down the alcohol content and also hydrating yourself at the same time. If you fancy a wine, you can also add an ice cube or two to a glass, or you could add soda water to make it a "spitzer'. Some wines just don't benefit from adding ice. So adding in several cubes, particularly to beer, will give you some good health benefits. You won't get as drunk and the hangover will be way less severe!
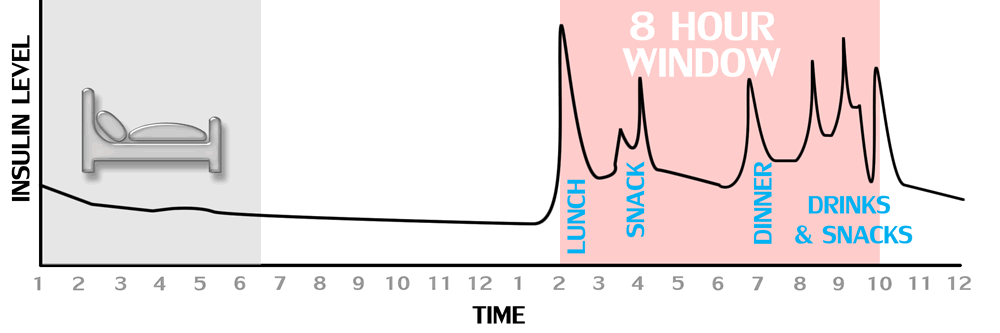
Drink and eat within a specific time window
Never try and drink on an empty stomach, it's always better to slow the absorption of alcohol and give you liver more time to handle the toxicants. The best way to eat and drink is to squeeze things into a tighter eating window. This is called intermittent fasting (or more appropriately, time restricted eating). If you consume breakfast at 7am and continue to eat throughout the day, followed by late night drinks, you are looking at 16-18 hours of eating & drinking, which of course comes with constant insulin spikes. You should ideally squeeze everything into 8 hours or less. This method of eating and drinking is proven to be considerably healthier than grazing all day. It give your body and your liver a rest.
Less Toxic Alcohol Options (if you're going to drink, go for these)
- Alcohol made from sugars and starches (no grains - top-shelf is always safest). Vodka, rum, tequila and most good gins.
- Champagne, White Wine, Red Wine - the antioxidants in red wine are nice, but a lot of wines acquire mycotoxins in the fermenting process.
- Other spirits (made from grains) such as good whisky.
- Lite beers
N-acetyl cysteine supplement
This is a medication that is used to treat paracetamol overdose. N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) is used by the body to build antioxidants. Antioxidants are vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients that protect and repair cells from damage. NAC is a precursor to glutathione. Taking NAC before you drink is known to reduce the toxic effects of alcohol and reduce your hangover (take least 200 milligrams 30 minutes before you drink). NAC is thought to work even better when combined with thiamine, or vitamin B1 (there is an excellent synthetic fat soluble version of B1 called bentfoimine). Vitamin B6 may also help to lessen hangover symptoms.
Vitamin C
Alcohol depletes your vitamin C, which is important for reducing oxidative stress in your liver caused by alcohol. Without high levels of vitamin C in your system, your liver will have to work harder.
Milk thistle supplement
Milk thistle is a flowering herb related to the daisy and ragweed. Milk thistle is sometimes used as a natural treatment for liver problems. The secret to milk thistle’s healing power is its ability to enhance glutathione. Never take paracetamol/tylenol with alcohol, it depletes glutathione and can even cause liver failure.
The "Skinny Bitch"

- Add a shot of quality vodka to a tall glass.
- Add ice.
- Top up with soda water.
- Squeeze in half a fresh lime.
- Add 2 drops of Angostura bitter (a great herb drink from Trinidad).
- Stir and enjoy.
You will stay hydrated (soda & ice) and also get some good acidity and vitamin C from the lime. The whole drink is about 70 calories, with the only carbs coming from the lime.
Red Wine Spritzer

- Fill a tall glass 1/2 full with ice.
- Pour red wine over ice until glass is 1/2 full.
- Fill remaining glass with soda water.
- Garnish with a slice of orange (optional)
- You can also garnish the glass with some powdered rock salt.
- Stir and enjoy.
You will stay hydrated (soda & ice) and get the benefits of red wine, without the hangover. This a a great alternative to a Sangria.
Bloody Mary

- Add a shot of quality vodka to a chilled glass.
- Pour in an unsweetened, organic tomato juice.
- Add a dash of Worcestershire sauce.
- Add a dash of Tabasco sauce.
- Sprinkle with some Himalayan sea salt.
- Garnish with a slice of tomato (optional).
This is a low calorie drink that even has some nutritional value. A good quality tomato juice will provide some antioxidants, mainly lycopene as well as vitamin C and potassium. Most bars will have a low quality tomato juice, so beware.
