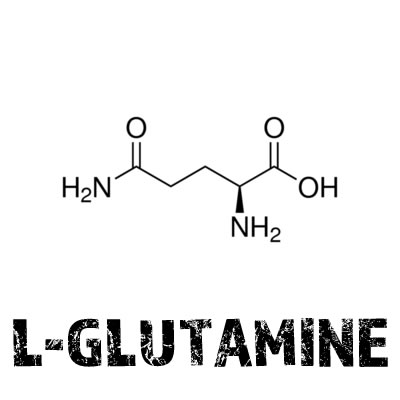
Glutamine
L-glutamine is a non-essential amino acid that is often simply called glutamine. It is produced by the body and is also found in food. But under certain conditions like illness, injury, or stress, our body fails to produce enough glutamine sufficient to meet our needs.
The dietary sources of glutamine includes protein-rich foods like beef, chicken, fish, dairy products, eggs, vegetables like beans, beets, cabbage, spinach, carrots, parsley, vegetable juices and also in wheat, papaya, brussel sprouts, celery, kale and fermented foods. L-glutamine is also available as an inexpensive powder supplement.
L-glutamine supplements are very common in the fitness industry (including bodybuilders) and it's needed by your body in large amounts as a protein building block. It promotes digestive health (often used to treat leaky gut) and boosts athletic performance. Glutamine is a major sources of energy for cells in the small intestine. In the gut, glutamine is needed for cellular production and cell growth, and to assist in the absorption and transport of nutrients.
Supplementation is recommended at 2-5g twice daily, and up to 10 grams daily for serious power athletes. If you take L-glutamine it’s a good idea to also supplement with B vitamins, especially vitamin B12, which controls glutamine in the body.
